
Ms. Tanaporn Ngamjit
Abstract :
Every curve, every line and every facet tell a story. It’s a procession where the minutest details can be an extraordinary influence, not only the physical spaces include perceptions and emotion. Embodying the notion that the smallest elements can have a profound impact on the overall experience of a motion. Within these layers have theme that resonates deeply with designing alike “The Devils is in the Details”
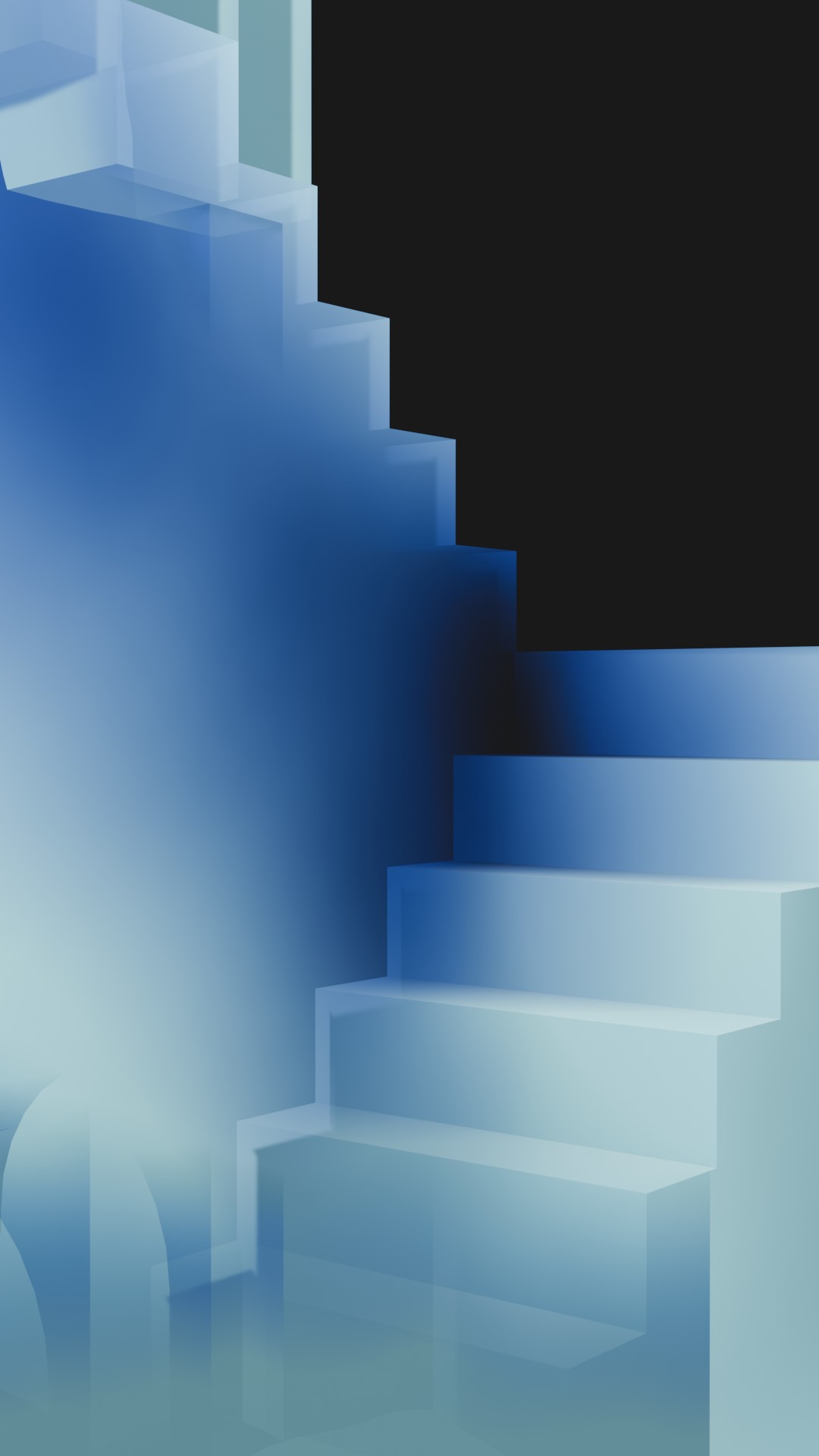
In the evolving of digital art and design, the integration of procedural geometry nodes has emerged as a powerful tool, offering creators a dynamic framework for generation complex structures with precision and efficiency. In the digital age, the pursuit of diversity has been elevated through the technologies such as procedural geometry and shading node within 3D design programs. The variety of procedural shading nodes generate a wide range of visual effects through the manipulation of mathematical. By mathematical expressions such as separate XYZ axis, color ramp, noise texture, math calculation and motion. However procedural shading nodes empower artists to unleash their creativity with unparalleled flexibility.
Objectives :
- To provide understanding of geometry shading structure nodes, functionality and manipulation of mathematical within context of proceduralism
- To empower artists and designers with the knowledge of structure nodes effectively in their creativity.
Conceptual Framework :
- The aim is to understand how shader nodes in Blender’s material editor facilitate the creation and manipulation of complex materials and textures for 3D rendering
- Review existing literature on computer graphics, shading models, and Blender’s material system.
- The process of generating a procedural shading nodes from a node builder using manipulation of mathematical, lighting, shading, and camera settings for rendering.
- Create visual diagrams of the relationships between different shader nodes, material properties, and their impact on the final rendered image.
Process / Methodology :
- Define the scope and purpose of the project.
- Begin with rough shapes to establish the overall form of the object in this scene.
- Refine the geometry by adding more complex shapes, edges, and surface details using tools like extrusion, sculpting, and Boolean operations.
- Apply procedural shading nodes to the model’s surface such as separate XYZ axis, color ramp, noise texture, math calculation and motion.
- Set up lights within the 3D scene to illuminate the objects.
- Render the scene to generate a high-quality sequence of images.
Techniques and Materials :
3D modeling, procedural shading nodes and motion graphic.
Result / Conclusion :
In conclusion, the journey from 3D procedural shading nodes has been challenging, resulting in the creation of an intriguing digital representation.
Reflecting on the results achieved, I’m pleased with the final outcome, which successfully. The attention to detail in procedural shading nodes, the artful application of textures, and the nuanced control of lighting have all contributed to the immersive quality of the rendered imagery.
References :
–